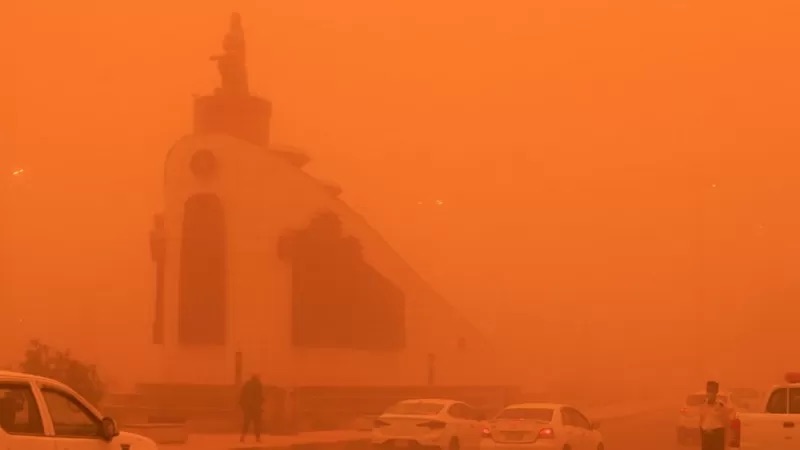
Although not a new phenomenon in the region, Iraq has faced an unprecedented number of dust and sandstorms since the beginning of this millennium. A few decades ago, Iraq would experience a storm or two a year during the winter season. However, this year, Iraq has already surpassed ten sandstorms during the past two months alone.
These meteorological events, which typically last three to five hours and can reach heights up to five thousand feet, are a hindrance to the average Iraqi civilian. These storms cause many to stay indoors for the duration of the event, followed by countless hours of cleaning as the grains of sand travel into even garment drawers. At times, the settling of the dust and sand particles can last for days. However, these dust and sandstorms have a more dire effect on the nation as a whole, including government and military operations. This piece will examine what is causing the increase of dust and sandstorms in Iraq, the socio-economic costs, and what actions can be taken to mitigate and potentially eliminate them.
Storms on the horizon
The storms cause fatalities around the country and long-term respiratory illnesses by inhaling sand and dust. This year, over ten thousand people were hospitalized, with at least five recorded deaths from the sandstorms that swept through Iraq. As a result of these dire conditions, this year, the Iraqi government shut down for many ministerial and provincial workers. The sandstorms even temporarily suspended all flights into the affected regions in Iraq, including the capital, Baghdad. These sandstorms are viewed as an aviation nightmare, as they drastically decrease the visibility for commercial and military pilots, often grounding all flights as the storm passes.
There appear to be no studies on the economic cost of dust and sandstorms in Iraq; however, a few have been conducted on the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region that put a dollar figure on the cost. The World Bank did the most comprehensive study in 2019, which found that the economic cost of premature deaths caused by sand and dust inhalation increased by 123 percent between 1990 and 2013 to $141 billion. The report explains that, in 2013, Iraq suffered 10,400 premature deaths due to dust in the air, which cost the economy almost $15 billion, or 3 percent of the year’s gross domestic product. The 2019 World Bank study estimates direct costs from grounded flights, lost crops, and production halted by government-ordered holidays at $13 billion, bringing the MENA region’s total economic cost from dust and sandstorms to over $154 billion annually.
Due to the inaction of the Iraqi government and civil society, the Environment Ministry stated in April that, over the past two decades, dusty days in Iraq have increased from 243 to 272 days per year, and warned that they are expected to reach three hundred days per year by 2050. Iraq is currently experiencing dust and sandstorms throughout all seasons of the year due to climate change, regional drought, desertification, and a decrease in water reserves—all factors that have led to dust accumulation. Studies have found that as much as 71 percent of agricultural land in the once “Fertile Crescent” is threatened by desertification due to climate change, which is decreasing the vegetation cover—the main factor for soil stabilization. According to a 2019 report by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), Iraq is the fifth-most vulnerable nation in the world to the effects of climate change.
Additionally, Iraqi officials claim that water reserves in Iraq have decreased over 50 percent over the past year due to poor rainfall and the water levels of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, which account for 98 percent of Iraq’s water reserves combined. The rivers are currently expected to dry up by 2040 if no actions are taken due to lower water levels and climate change.
The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers originate in Turkey and flow to the Shatt al-Arab Basin in Iraq, while the Euphrates crosses through Syria before flowing to Iraq. Due to the Iraqi government’s inaction, plans by Turkey that alter river flows are major contributing factors to the drying up in Iraq. The Turkish government, which is constructing hydropower plants on the banks of the rivers, boasts that their plans are an abundant source of carbon-free electricity. However, experts warn that the dam is taking a human and environmental toll. This, alongside the lack of rainfall, which is decreasing vegetation cover, makes Iraq vulnerable to the microbursts of winds, expanding dust and sandstorms.
What can be done?
First and foremost, it’s crucial to reiterate the importance that Iraq takes expedited measures to address all factors contributing to the increase in dust and sandstorms. The Iraqi government must adopt a cultural and legislative overhaul that is more eco-conscious, so that every citizen is self-aware of how they contribute to the demise of an inhabitable Iraq.
Possible solutions include legislation that re-cultivates desertified lands by increasing agriculture and encouraging farmers to plant orchards and other crops around cities, towns, and villages. In the 1980s, an estimated thirty million date palm trees were growing in Iraq. However, due to actions taken by the Ba’athist regime under Iraqi Dictator Saddam Hussein and a chaotic post-2003 invasion, Iraq currently has less than twelve million palm trees. In 1995, Iraq had some of the world’s most productive soils, with agriculture representing more than 18 percent of the nation’s economy. Today, however, it accounts for less than 2 percent. Modern irrigation techniques—such as drip and spray irrigation—need to also become the norm in Iraq, for these techniques significantly reduce water loss by farmers.
Other solutions include the Iraqi government creating environmental reserves with diverse plants and animals far from population centers. These reserves will serve as more vital vegetation cover and will also serve as a catalyst for new ecosystems to prosper in Iraq. The Iraqi government should also adopt legislation that eliminates the unauthorized exploitation of natural resources, including sand, which is used for building materials as the encroachment of sand destabilizes the ground, allowing microbursts of wind to carry more sand during the storms.
This phenomenon threatening life in Iraq isn’t unprecedented, as many of Iraq’s neighboring nations have already commenced addressing the threat of climate change. Iraq can benefit from the experiences of the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Turkey, and others, and utilize published studies to see what methods may be more effective in addressing climate change within its borders. To effectively combat the threat of climate change in the MENA region, it is imperative that all neighboring nations work together to devise a climate change plan that considers the safeguarding of all inhabitants of the region.
The truth is that, in order to combat climate change effectively and in a timely matter, Iraq cannot combat it alone. Upon becoming a party to the Paris Agreement at COP26, the United Nations called on the international community to stand in solidarity with Iraq as it combats climate change. This can be done through funding from the international community, coming with expert-set stipulations and tracked through international bodies like UNEP.
Through some of the above-proposed methods and more research, the Iraqi government and population can take the necessary steps to protect their country from the changing climate and safeguard Iraq for future generations.
Muhammad Baqir Muhyedeen is the policy program manager at the Muslim Public Affairs Council (MPAC) and an expert on Iraqi affairs. Follow him on Twitter: @mbmdeen.